How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone piloting, from pre-flight checks and control mastery to advanced navigation and photography techniques. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills.
Understanding drone operation involves more than just pushing buttons; it requires a solid grasp of safety protocols, flight mechanics, and legal considerations. This comprehensive guide breaks down each stage of the process, providing clear instructions and helpful tips to ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience. We’ll explore practical techniques for navigating, capturing stunning aerial footage, and handling potential emergencies.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before operating a drone, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful flight. This involves verifying various aspects of the drone and its environment to mitigate potential risks. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents, damage to property, or even injury.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist includes verifying battery levels, GPS signal strength, and assessing weather conditions. It’s also essential to visually inspect the drone for any physical damage or loose components.
A step-by-step procedure for a safe pre-flight inspection involves systematically checking each item on the checklist. This ensures that nothing is overlooked and that the drone is in optimal condition for flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and successful flights.
| Check Item | Action | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check the battery indicator on the drone and remote. Ensure sufficient charge for the planned flight duration. | ||
| GPS Signal | Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired. The number of satellites locked should be sufficient for stable flight. | ||
| Propellers | Visually inspect propellers for damage, cracks, or loose attachments. | ||
| Gimbal | Check the gimbal for smooth movement and ensure it is properly secured. | ||
| Weather Conditions | Check wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or fog. | ||
| Drone Body | Inspect the drone’s body for any damage or loose parts. | ||
| Remote Control Batteries | Ensure the remote control batteries are sufficiently charged. | ||
| Flight Area | Verify the flight area is clear of obstacles and people. Check for any airspace restrictions. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the basic controls and flight modes of your drone is paramount for safe and efficient operation. This section will cover the fundamental controls and various flight modes available on most drones.
Drone Controls, How to operate a drone
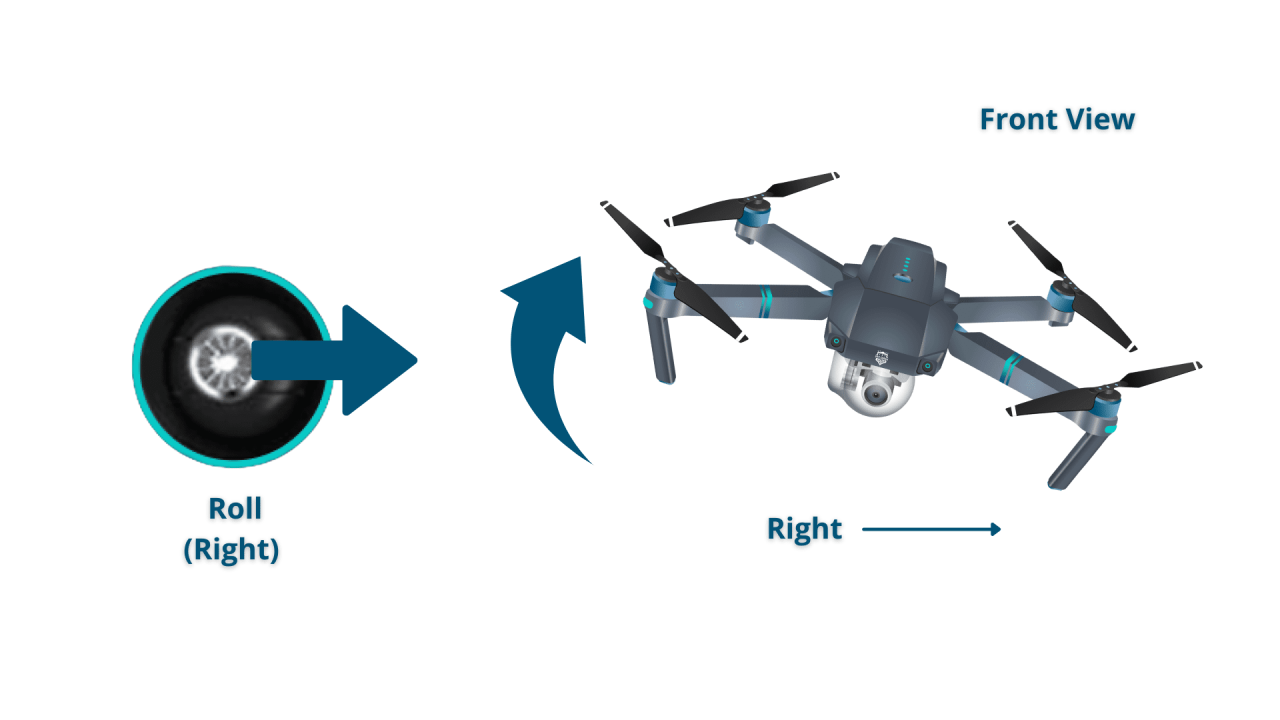
Standard drone controls typically involve two joysticks. One controls the drone’s altitude (throttle) and forward/backward movement (pitch), while the other controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and left/right movement (roll). Understanding these controls is essential for maneuvering the drone effectively.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer different flight modes, such as beginner mode (limiting speed and responsiveness), sport mode (allowing for faster and more agile maneuvers), and GPS mode (providing autonomous flight features). Choosing the appropriate flight mode depends on the pilot’s skill level and the complexity of the flight operation.
Smooth Drone Maneuvers
Tips for smooth and controlled maneuvers include using gentle stick movements, avoiding abrupt changes in direction, and practicing in a safe, open area. Smooth operation ensures the safety of the drone and avoids potential accidents.
Drone Controller Visual Representation
Imagine a drone controller with two joysticks. The left joystick controls altitude (up/down) with the vertical axis and forward/backward movement with the horizontal axis. The right joystick controls yaw (rotation) with the vertical axis and left/right movement with the horizontal axis. Several buttons are typically located around the joysticks, including power, camera control buttons, and mode selection buttons. The controller also features an LCD screen displaying various flight parameters such as battery level, GPS signal, and flight mode.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Safe takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and damage. This section Artikels the steps involved in each phase of flight.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Ensure GPS signal is locked.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Once airborne, transition to hovering.
Stable Hovering
Maintaining stable hovering involves making small, precise adjustments to the controls to compensate for wind and other external factors. Practice is key to achieving smooth and consistent hovering.
Safe Landing Procedure
- Slowly decrease the throttle to descend.
- Maintain a stable descent rate.
- Gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Abrupt throttle movements: Can lead to uncontrolled ascents or descents.
- Ignoring wind conditions: Can result in the drone being blown away.
- Landing on uneven surfaces: Can damage the drone’s landing gear.
- Insufficient battery: Can lead to a mid-flight power failure.
Drone Flight Planning and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Effective flight planning is essential for safe and efficient drone operations. This includes considering factors such as airspace restrictions, potential hazards, and the desired flight path.
Flight Planning Importance

Proper flight planning minimizes risks and ensures that the flight is conducted safely and legally. This includes identifying potential hazards and choosing appropriate flight parameters.
Flight Planning Software/Apps
Several software applications and mobile apps are available to assist with flight planning. These tools allow pilots to create detailed flight plans, including waypoints and altitude profiles.
GPS and Visual Navigation
Navigation can be achieved using GPS coordinates for precise positioning and visual references for situational awareness. Combining both methods provides a robust and reliable navigation system.
Navigation Techniques Comparison
Waypoint navigation involves pre-programming a series of points for the drone to follow, while following a pre-planned route involves creating a continuous path for the drone to traverse. Waypoint navigation offers greater flexibility, while pre-planned route navigation is ideal for repetitive tasks.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
Understanding drone camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section explores various camera settings and provides tips for optimal image capture.
Drone Camera Settings and Modes
Drone cameras typically offer a range of settings, including aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and various shooting modes (photo, video, timelapse). Understanding these settings is key to controlling image quality and creative expression.
Tips for High-Quality Photos and Videos
Tips include maintaining a stable platform (avoiding camera shake), using appropriate exposure settings for the lighting conditions, and composing shots effectively. Consider using ND filters to reduce light and achieve smoother video footage.
Stable Shots and Avoiding Camera Shake
Techniques for achieving stable shots include using a gimbal, flying in calm conditions, and practicing smooth and controlled maneuvers. Post-processing software can also be used to stabilize footage.
| Setting | Description | Effect on Image | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aperture | Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. | Affects depth of field and image brightness. | Wide aperture for blurred backgrounds (portraits), narrow aperture for sharp focus (landscapes). |
| Shutter Speed | Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. | Affects motion blur and image brightness. | Fast shutter speed for freezing motion, slow shutter speed for motion blur. |
| ISO | Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. | Affects image noise and brightness. | Low ISO for low noise in bright conditions, high ISO for brighter images in low light (increased noise). |
Emergency Procedures and Troubleshooting
Knowing how to handle emergencies and troubleshoot common drone malfunctions is essential for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for various emergency situations.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and communication issues. Causes can range from environmental factors to mechanical problems or software glitches.
Emergency Situation Handling
Procedures for handling emergencies include initiating an immediate return-to-home (RTH) function if available, attempting a controlled landing, and contacting support if necessary. Prioritizing safety is paramount in all emergency situations.
Drone Crash Recovery
Tips for recovering a drone from a crash involve carefully inspecting the drone for damage, repairing any broken components, and recalibrating the drone if necessary. Safety should always be prioritized during recovery efforts.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone found on the UAV Drone Fair website. This will equip you with the knowledge to safely and effectively handle your drone, ensuring both a positive experience and responsible operation.
Emergency Procedures Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart starting with “Drone Malfunction Detected?”. If yes, it branches to “Low Battery?”, “GPS Loss?”, “Motor Failure?”, and “Other Malfunction?”. Each branch leads to specific troubleshooting steps, such as “Initiate RTH”, “Attempt Controlled Landing”, “Inspect for Damage”, or “Contact Support”. The flowchart ultimately leads to “Drone Secured” or “Seek Professional Assistance”.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to local drone regulations and laws is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation. This section highlights key legal considerations.
Importance of Adhering to Regulations
Compliance with regulations ensures safe airspace operations, protects privacy, and prevents legal repercussions. Ignorance of the law is not a valid excuse.
Permits and Licenses

Depending on the location and intended use, specific permits or licenses may be required for drone operation. These requirements vary by jurisdiction and should be researched thoroughly before flying.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Several airspace restrictions and no-fly zones exist near airports, government buildings, and other sensitive areas. These restrictions must be strictly adhered to.
Essential Legal Considerations
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities.
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
- Respect privacy and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
- Fly within legal airspace limitations.
- Maintain situational awareness and avoid hazards.
- Understand and comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
Mastering the art of drone operation opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying and inspection tasks. By following the guidelines and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the skies safely and confidently, capturing stunning visuals and pushing the boundaries of your aerial adventures. Remember, responsible drone piloting is key, so always prioritize safety and legal compliance.
FAQ Compilation
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge.
What should I do if I lose the GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home function. If this fails, attempt to visually guide the drone back, prioritizing a safe landing.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures.
